2019年度 成果出版
2019年度のフィールドワーク・レポートを出版いたしました。『臨地 2019』PDF版をご希望の方は支援室までお問い合わせください。『創発 2019』PDF版は下記のリンクよりダウンロードできます。 書名『臨地 2019』院⽣海外臨地調査報…
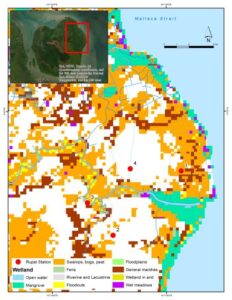
Photo 1:Location of monitoring station groundwater monitoring station (GWMS) 1 in Cinggem; GWMS 2 in Parit Kebumen; GWMS and tides station in number 3, Tanah Runtuh; weather station in Pangkalan Nyirih (4).
Tropical peatlands are subjected to anthropogenic disturbance, which deteriorates the environment and alters the hydrological properties of peatlands. Peat hydrological properties are among the most important factors in evaluating and managing the peatland area. Hydrological properties in peatlands are related to other physical processes, making them complex. One of the peatland hydrological components is groundwater, which plays a significant role in maintaining equilibrium in the peatland ecosystem. The over-draining activity for plantation, domestic use, and land use changes threaten the environmental equilibrium.
There are various attempts to understand the peatland environment, especially its hydrological properties. But, so far, no detailed study covers small peat islands. Seawater intrusion as part of the hydrological process in peat islands has never been recognized before. Rupat Island is a small island that is bigger than Singapore. It consists of peatland and any other lithology that annually suffers from peat fire. Furthermore, many areas on this island have limited fresh water supply. Studies have yet to be conducted on this topic fully. This is important as it can be a role model for similar cases in which small islands suffer from human-induced environmental pressure and climate change.
This stage of research aims to install one meteorological station that measures precipitation and air temperature, three shallow-water monitoring wells, a tide monitoring station, and collect physical water quality data.

Photo 2:Soil core sampling from the borehole was made in Parit Kebumen to measure the pH and EC at every 20 cm depth.
Rupat Island is a small island in Riau, bordering Indonesia and Malaysia. It comprises several ethnic groups, such as Orang Asli (Akit), Melayu, and Javanese. The island’s economy mostly relies on the plantation industry, which produces palm oil, rubber, and acacia. Almost no natural forest is left, mostly converted into plantations. With the increase in population, environmental pressure will increase soon. In that case, a solution to overcome the upcoming problems is needed; one way is by collecting environmental data to understand the current conditions and estimate the future.
Environmental scientific data on Rupat Island is very scarce. Until 2023, a PM 2.5 and rainfall station was installed in the central part of the island as part of CSEAS and BRIN research collaboration. In addition, in this fieldwork, I installed one meteorological station far from the previously installed station. The station was in Pangkalan Nyirih Village. The consideration for choosing the location is related to the spatial pattern of rainfall on the island. During the stay, rainfall differs between the newly installed and the previous one. So, the distribution of the rainfall monitoring station will correspond to the rainfall spatial pattern.
Along with the rainfall station, a tide monitoring station was installed in the Morong strait, which divided the island into two parts and connected it to the sea. The water in this strait is very brackish because of the mixture of land and seawater. Many sea creatures and mangroves can be found in this aquatic environment. There are two high tide cycles with a 12-hour time span, and they shift with different seasons.
Three shallow groundwater monitoring stations (4 meters deep) were installed on different land uses (photograph 1). One was installed in a peatland with a palm oil field in Cinggem Village. The other is in a peatland with a rubber field in Parit Kebumen village. The last station is located near the peatland on the side of Morong Strait, which is a settlement in Dusun Tanah Runtuh. The location of the station was chosen based on spatial variability.
Along with the installation of stations, water physical parameters measurement was conducted for shallow groundwater, deep groundwater, surface water, and seawater. The parameters measured were pH, electric conductivity (EC), total dissolved solids (TDS), water temperature, resistivity, and salinity. Based on the measurement and observation, most areas were influenced by intrusion, which was indicated by brackish water (high EC and salinity). It was presumably affected by tides and the lithological unit building the area. Soil EC and pH were measured every 20 cm depth (photograph 2).
Another fieldwork will be conducted to install a new deep groundwater monitoring station, followed by measuring water physical parameters in different seasons. Water samples to analyze geochemistry may be taken. Also, people’s understanding of seawater intrusion and its impact on daily life will be assessed.
Copyright © 附属次世代型アジア・アフリカ教育研究センター All Rights Reserved.